
Financial Stability Committee’s Decision
The Financial Stability Committee (FSC) of the NBG decided to set the cycle-neutral countercyclical capital buffer (base rate) at 1%. During the previous meeting, according to Basel Committee Recommendation, the FSC committee announced the introduction of positive cycle-neutral countercyclical capital buffer. While a base rate for countercyclical capital buffer was zero in normal times and increased in case of excess credit activity, hereafter, a base rate for positive cycle-neutral countercyclical capital buffer will be set at 1% in normal periods. Countercyclical capital buffer will be increased in the event of excess credit activity and released in the stressful periods.
Some countries have already introduced positive buffer ranging from 1% to 2% as a base rate. The committee decided to set cycle-neutral countercyclical capital buffer at 1% considering international experience and characteristics of financial sector. 12 months period is given for banks to satisfy the requirement.
As a result of financial stability policy implemented by the NBG, the financial sector remains resilient and continues smooth lending to the economy. As of January 2023, banks maintain healthy capital and liquidity indicators, while the asset quality improved compared to previous year. Similar to the previous year, banks started 2023 year with a solid profit, which was supported by the credit activity and small credit losses. Improved financial indicators allowed majority of banks to recover released capital buffers. Therefore, significant share of banks will be able to satisfy countercyclical capital buffer requirement with internal resources, using existing profitability and capital buffers. Considering the risks coming from the current regional situation, the accumulation of capital buffers will help banks to mitigate risks and, in the periods of stress, it will promote smooth lending and fast economic recovery.
Credit activity will be in line with nominal economic growth in the current year. The annual growth rate of credit portfolio in January 2023, excluding the exchange rate effect, amounted to 13.3%, which was mainly driven by the growth of business loans. The Credit-to-GDP ratio has been decreasing during the last two years, which reflects the impact of high economic growth and exchange rate appreciation. Consequently, in the fourth quarter of 2022, the Credit-to-GDP ratio is below its long run trend, however, it should be noted that existing level of the Credit-to-GDP ratio in Georgia is still quite high compared to peer countries. According to Committee’s assessment, if the existing tendency of credit activity continues, the growth of credit portfolio will be in line with nominal economic growth in the current year.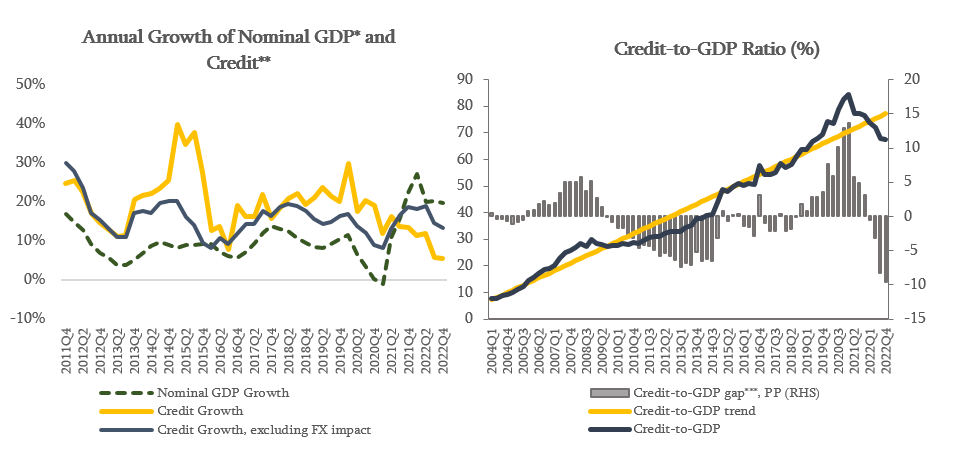
Source: NBG; Geostat
* Nominal GDP growth reflects the YoY GDP growth of the last 4 quarters.
** Credit includes loans directly issued by commercial banks and microfinance institutions as well as bonds issued domestically by the non-financial sector.
*** Credit-to-GDP gap is the deviation of Credit-to-GDP ratio from its long-run trend. The trend is estimated using HP filter in line with the Basel recommendations
The National Bank of Georgia continues monitoring the country's financial stability and assessing domestic and foreign risks. If necessary, it will use all available instruments to minimize the possible risks.
The Financial Stability Committee's next meeting will be held on May 31, 2023.