Resolution
The aftermath of the 2007-2008 global financial crisis exposed the need for structural reform to create an advanced model of financial system stability. To address one of the shortcomings identified, the EU adopted the Banking Recovery and Resolution Directive (BRRD) in 2014, which introduced a liquidation alternative - a rehabilitation mechanism to mitigate the expected adverse systemic impact from a distressed financial institution.
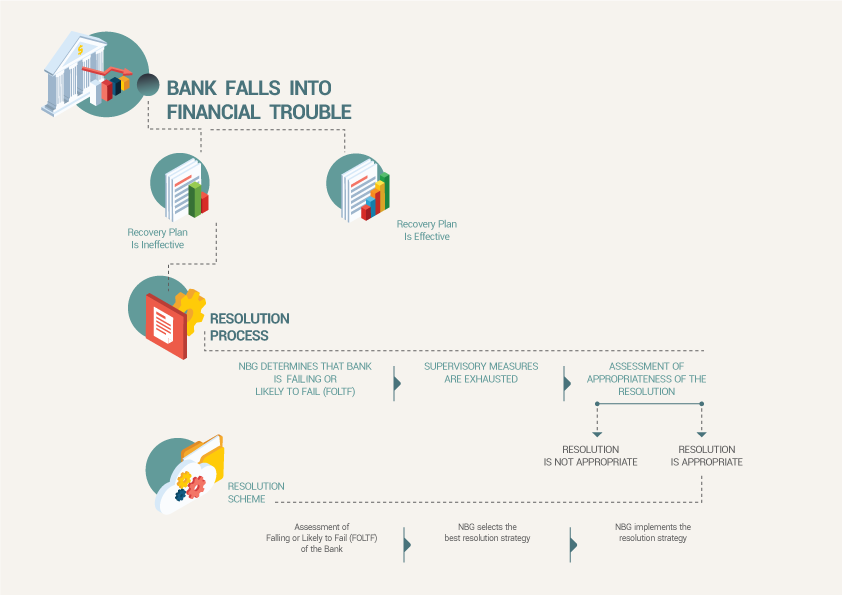
The resolution authority is represented by the National Bank of Georgia, which implements the resolution using the resolution tools. In particular, the resolution is restructuring the commercial bank in a way that the public interest will be protected, including, maintaining the critical functions of the commercial bank, ensuring financial stability and minimizing costs to taxpayers.
Critical Functions:
- Deposits – acceptance of deposits by the bank from retail and corporate customers and administration of deposit accounts. When assessing the criticality of the deposit-taking function, the types and number of depositors of the bank, the types of deposits and the expected impact of interruption/discontinuation of the function on other banks with the same function, as well as the share of insured deposits in total deposits of the bank provided by the Law of Georgia "On Deposit Insurance System" should be taken into account;
- Lending – issuance of consumer, mortgage, unsecured and/or other types of loans by the bank to retail and corporate customers and administration of relevant accounts. When assessing the criticality of the bank's lending function, at least the size of the loan portfolio, including the balance of secured and unsecured loans, the number and types of borrowers, maturity and liquidity of issued loans should be taken into account;
- Payment services, Cash, Settlement, Clearing, Custody services- provision of payment services by the bank for retail and corporate customers, as well as provision of clearing and settlement services;
- Security market services – performance of the function of a financial intermediary by the bank, brokerage activities and/or activities permitted for banks as defined by the Law of Georgia "On the Securities Market";
- Wholesale financing - funds received by the bank from financial institutions and issued to financial institutions, which does not include intra-group positions. In assessing the criticality of the function provided for in this subsection, the bank shall at least take into account the size, maturity, purpose, substitutability and market share of both funds received and issued.
In light of the Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) in Georgia, bank recovery and resolution (BRRD) framework was adopted based on the recommendations of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank: "Key Attributes of Effective Resolution Regimes for Financial Institutions" and BRRD 2014/59/EU on Bank Recovery and Resolution. Following the reform that entailed the introduction of the resolution mechanism, the National Bank acquired the resolution function for commercial banks. The resolution framework aims to raise the risk management culture in the banking sector, respond to the financial crisis timely, ensure the continuity of critical economic functions and maintain financial stability at the system level.
When does the bank resolution occur?
Resolution is preferable to liquidation for a bank facing financial difficulties, when, liquidation is more harmful to financial stability and the country's economy than the resolution.
In such cases, various resolution instruments are used, which:
- Ensures the continuity of the commercial bank's critical functions;
- Maintains financial stability;
- Fully or partially recovers the commercial bank.
If, as a result of the resolution, the commercial bank cannot be restructured accordingly, the bank will be liquidated.