
Financial Stability Committee’s Decision
As a result of financial stability policy implemented by the National Bank of Georgia, the financial sector remains resilient and continues smooth lending to the economy. As of April 2022, banks maintain healthy capital and liquidity buffers, while asset quality has improved compared to the previous year. Similar to the preceding year, banks started 2022 with solid profitability, which was driven by strong credit activity and small loan loss provisions. Improved financial indicators enabled most of the banks to recover released capital buffers.
Along with the Russia-Ukraine war, uncertainty regarding macroeconomic trends in the region remains high, however, Georgian financial system is ready to withstand the stress. As it was shown in the stress test results released in December 2021, banking sector remains solvent even under severe and extreme risk scenarios. Despite potential losses, capital adequacy on aggregate level is above the minimum regulatory requirement and existing capital buffers are enough to absorb losses. Direct sanctions were imposed only on one subsidiary of Russian bank and this problem was soon resolved by selling parts of assets and liabilities to other banks. Besides, if needed, the National Bank of Georgia will implement countercyclical measures as it has done during the pandemic, which contributed to financial sector stability. Current macroeconomic events once again outlined correct, forward-looking policy pursued by the NBG to reduce dollarization.
The Financial Stability Committee of the NBG decided to leave the countercyclical capital buffer unchanged, at 0%. The annual growth rate of credit portfolio in April 2022, excluding the exchange rate effect, amounted to 18.3%, which is mainly driven by the growth of business loans and from the currency perspective, by the lending in national currency. The Credit-to-GDP ratio decreased during the last year, which reflects the impact of high economic growth and exchange rate appreciation. Consequently, in the first quarter of 2022, the Credit-to-GDP ratio is slightly below compared to its long run trend. However, it should be noted that existing level of the Credit-to-GDP ratio is still high in comparisson with peer countries. The Financial Stability Committee considers that it is important to have a credit growth that is in line with economic activity and supports sustainable growth of the economy and the welfare of society, without accumulating excessive financial stability risks.
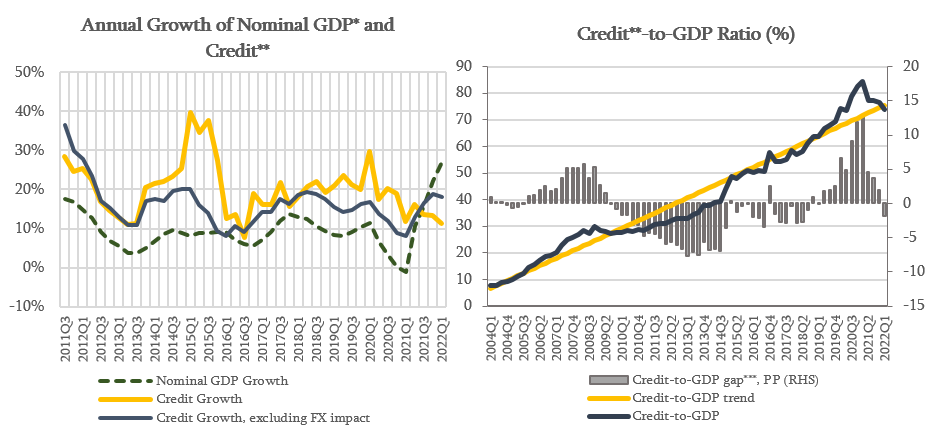
Source: NBG; Geostat
* Nominal GDP growth reflects the YoY GDP growth of the last 4 quarters.
** Credit includes loans directly issued by commercial banks and microfinance institutions as well as bonds issued domestically by the non-financial sector.
*** Credit-to-GDP gap is the deviation of Credit-to-GDP ratio from its long-run trend. The trend is estimated using HP filter in line with the Basel recommendations
The National Bank of Georgia continues monitoring the country's financial stability and assessing domestic and foreign risks. If necessary, it will use all available instruments to minimize the possible risks.
The Financial Stability Committee's next meeting will be held on September 28, 2022.